Running apps on Ubuntu 24.04 gets a boost with Docker, a free tool that simplifies containerized development.
Perfect for developers and sysadmins, it lets you create, deploy, and manage applications in lightweight, portable containers.
In 2025, installing Docker on Ubuntu 24.04 is straightforward, syncing seamlessly with the latest updates.
This guide covers the best ways to get started, so let’s dive in.
How to Install Docker on Ubuntu 24.04
Choose your method to install Docker Engine, all optimized for Ubuntu 24.04:
Method 1: Install via Official APT Repository (Recommended)
- Open your terminal.
- Update package index and install prerequisites:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install ca-certificates curl
- Add Docker’s GPG key:
sudo install -m 0755 -d /etc/apt/keyrings
sudo curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg -o /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.asc
sudo chmod a+r /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.asc
- Set up the Docker repository:
echo "deb [arch=$(dpkg --print-architecture) signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/docker.asc] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu $(. /etc/os-release && echo "$VERSION_CODENAME") stable" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.list > /dev/null
- Install Docker:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io docker-buildx-plugin docker-compose-plugin
- Verify it’s running:
sudo systemctl status docker
- Test with a sample container:
sudo docker run hello-world
Method 2: Install via Snap (Quick Alternative)
- Open your terminal.
- Install Docker with Snap:
sudo snap install docker
- Launch it and test:
docker run hello-world
Tip: APT offers the latest stable release (26.0.0 as of Feb 2025) with full control, Snap is simpler but may lag slightly in updates.
What Makes Docker Special
Docker, launched in 2013 by Docker Inc., is an open-source platform that revolutionizes app deployment with containers. Lighter than virtual machines, it’s a favorite for developers and sysadmins on Ubuntu:
- Portable, lightweight containers
- Resource isolation for stability
- Image-based app packaging
- Flexible networking options
- Easy scalability
System Requirements
- OS: Ubuntu 20.04 or newer (optimized for 24.04)
- Processor: 64-bit CPU
- Memory: 4GB RAM (8GB recommended)
- Storage: 1GB free space (plus container images)
- Internet: Required for initial setup
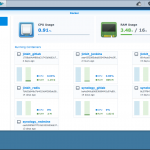
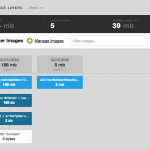
Docker in Action: Screenshots
More Ubuntu Tools
Check out: Bitwarden for Ubuntu, TeamViewer for Ubuntu, Visual Studio Code for Ubuntu.